| Ligne 66 : | Ligne 66 : | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" valign="middle" bgcolor="#999999" |Création de l’objet | | align="center" valign="middle" bgcolor="#999999" |Création de l’objet | ||
| − | | align="left" valign="middle" |int rxPin = | + | | align="left" valign="middle" |int rxPin = D5; |
| − | int txPin = | + | int txPin = D6; |
SdsDustSensor sds(rxPin, txPin); | SdsDustSensor sds(rxPin, txPin); | ||
| Ligne 110 : | Ligne 110 : | ||
delay(10000); | delay(10000); | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Astuce: il | + | Astuce: il est possible RX et TX soient inverser, dans ce cas il vous suffit d'inverser D5 et D6 dans votre code.<br /> |
| − | |||
| − | <br /> | ||
==Exemple== | ==Exemple== | ||
| − | < | + | <br /><syntaxhighlight lang="arduino" line="1"> |
| − | + | #include "SdsDustSensor.h" | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | int rxPin = D5; | ||
| + | int txPin = D6; | ||
SdsDustSensor sds(rxPin, txPin); | SdsDustSensor sds(rxPin, txPin); | ||
| − | |||
void setup() { | void setup() { | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serial.begin(9600); | ||
| + | sds.begin(); | ||
| − | + | Serial.println(sds.queryFirmwareVersion().toString()); | |
| − | + | Serial.println(sds.setActiveReportingMode().toString()); | |
| − | + | Serial.println(sds.setContinuousWorkingPeriod().toString()); | |
| − | |||
| − | Serial.println(sds.queryFirmwareVersion().toString()); | ||
| − | |||
| − | Serial.println(sds.setActiveReportingMode().toString()); | ||
| − | |||
| − | Serial.println(sds.setContinuousWorkingPeriod().toString()); | ||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
void loop() { | void loop() { | ||
| + | |||
| + | PmResult pm = sds.readPm(); | ||
| + | if (pm.isOk()) { | ||
| + | Serial.print("PM2.5 = "); | ||
| + | Serial.print(pm.pm25); | ||
| + | Serial.print(", PM10 = "); | ||
| + | Serial.println(pm.pm10); | ||
| + | Serial.println(pm.toString()); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | else { | ||
| + | Serial.print("Could not read values from sensor, reason: "); | ||
| + | Serial.println(pm.statusToString()); | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | delay(500); | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
| − | + | </syntaxhighlight><br /> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{Tuto Status | {{Tuto Status | ||
|Complete=Draft | |Complete=Draft | ||
}} | }} | ||
Version du 10 décembre 2020 à 12:12
Capteur de particules SDS011
Capteur basé sur un laser SDS011 PM2.5/PM10 permettant de tester avec précision et fiabilité la qualité de l'air
Description longue
Principe:
Ce capteur est basé sur un laser SDS011 PM2.5/PM10 permettant de tester avec précision et fiabilité la qualité de l'air.
Ce laser fiable, rapide et précis mesure le taux de particules dans l'air compris entre 0,3 et 10 µm.
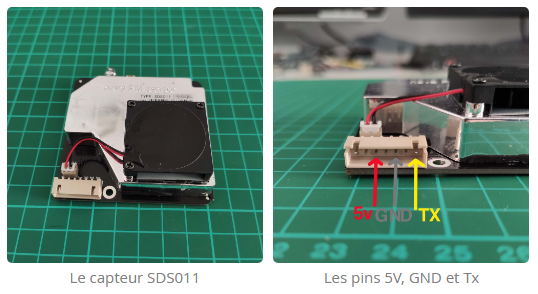
Il communique avec un microcontrôleur compatible via une sortie UART.
Le capteur est livré sans cordon de raccordement mais peut être utilisé avec des cordons de prototypages M/F par exemple.
Une librairie Arduino sous licence GPL est disponible en téléchargement .
Librairie Nova_SDS011 Sensor
Le capteur SDS011 peut également être utilisé sur un PC via un convertisseur USB vers UART TTL inclus.
Caractéristiques :
Alimentation: 4,7 à 5,3 Vcc
Consommation:
- au travail: 70 mA ±10mA
- au repos: < 4 mA
Plage de mesure: 0 à 999,9 µg/m³
Résolution: 0,3 µg/m³
Fréquence d'échantillonage: 1 Hz
Température de service: -10 à 50 °C
Humidité de service: 70 % RH maxi
Pression atmosphérique: 86 KPa à 110 KPa
Dimensions: 71 x 70 x 23 mm
Bibliothèque :
Pour utiliser facilement ce capteur, nous vous conseillons d'utiliser la bibliothèque sds-dust-sensors-arduino-library que vous trouverez ici, en cliquant sur ce lien
Câblage
Code Minimal
| Avant le Setup | Importation de la bibliothèque | #include "SdsDustSensor.h" |
| Création de l’objet | int rxPin = D5;
int txPin = D6; SdsDustSensor sds(rxPin, txPin); | |
| Dans le Setup | Démarrage de l’objet | Serial.begin(9600);
sds.begin(); Serial.println(sds.queryFirmwareVersion().toString()); Serial.println(sds.setActiveReportingMode().toString()); Serial.println(sds.setContinuousWorkingPeriod().toString()); |
| Dans le Loop | Utilisation | PmResult pm = sds.readPm();
if (pm.isOk()) { Serial.print("PM2.5 = "); Serial.print(pm.pm25); Serial.print(", PM10 = "); Serial.println(pm.pm10); Serial.println(pm.toString()); } else { Serial.print("Could not read values from sensor, reason: "); Serial.println(pm.statusToString()); } delay(10000); |
Astuce: il est possible RX et TX soient inverser, dans ce cas il vous suffit d'inverser D5 et D6 dans votre code.
Exemple
#include "SdsDustSensor.h"
int rxPin = D5;
int txPin = D6;
SdsDustSensor sds(rxPin, txPin);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
sds.begin();
Serial.println(sds.queryFirmwareVersion().toString());
Serial.println(sds.setActiveReportingMode().toString());
Serial.println(sds.setContinuousWorkingPeriod().toString());
}
void loop() {
PmResult pm = sds.readPm();
if (pm.isOk()) {
Serial.print("PM2.5 = ");
Serial.print(pm.pm25);
Serial.print(", PM10 = ");
Serial.println(pm.pm10);
Serial.println(pm.toString());
}
else {
Serial.print("Could not read values from sensor, reason: ");
Serial.println(pm.statusToString());
}
delay(500);
}Pages liées
Draft